- How is electrification playing out in the Automotive Industry?
The Automotive Industry is experiencing a shift from internal combustion engines (ICE) to electric vehicles (EVs). Governments worldwide are promoting carbon neutrality and implementing stricter emission norms, leading to incentives and credits for electric vehicles. The pace of this shift varies by region and customer segment. China is leading in battery electric vehicles (BEVs), followed by the US and EU. Japan relies on hybrid electric technology, while India is seeing an increase in EV adoption for two-wheelers. Fuel cell EVs are being considered for commercial vehicles, and research is focused on alternative battery chemistries. MathWorks supports this transition by providing tools for EV development and partnering with OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers.

Rashmi Gopala Rao, automotive industry manager
As for the Benelux region, we mainly see government incentives for the development and retrofitting of charging infrastructure to meet and exceed grid capacity and adaptive energy demands, R&D programmes for the development of electrical technologies, from motor control to battery management, as well as integrating renewable energy into the power grid.
- How is the trend in electrification transforming the Automotive Industry?
The trend in electrification is transforming the entire value chain of the Automotive Industry. OEMs are investing in engineering talent and supply chains for EVs and shifting towards in-house components and software development. This allows for better cost control and differentiation. Tier-1 suppliers design and manufacture batteries, inverters, and motors, often packaging them as e-axles for higher efficiency. Engineering service providers play a role in supporting development and verification tasks. Traditional petroleum companies are pivoting to charging infrastructure as EV adoption rises. MathWorks offers system-level simulation software to facilitate the design and development of safe vehicles with software, integrating multi-domain systems and reducing reliance on prototypes.
- What are some of the engineering challenges in the development of electrification?
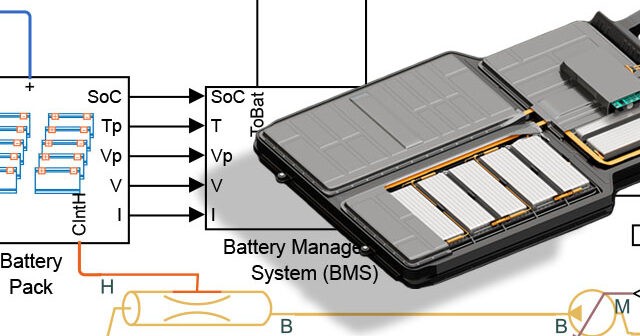
There are several engineering challenges in the development of electric vehicles. System engineers face trade-offs when selecting the right battery and motor while considering the target cost and price. Thermal management is crucial to prevent battery aging and ensure optimal performance. Software engineers focus on reusing artifacts, generating optimized code, and creating continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines. Systems integrators tackle the integration of different components to achieve a seamless drivetrain. MathWorks provides solutions tailored to different engineering roles, such as Powertrain Blockset™ and Simscape™ for system and component engineering. The company enables software engineers with end-to-end workflow solutions for algorithm development, implementation, and verification.

Mohamed Anas, regional technical manager, MathWorks
- What is the impact of software-defined vehicles on the Automotive Industry?
Software-defined vehicles refer to vehicles that utilize software and digital technologies to control and manage various aspects of the vehicle’s functionality. These vehicles rely on software systems and computational power to control and configure their hardware components, allowing for greater flexibility, upgradability, and customization. This shift is driven by customer expectations for clean, safe and connected mobility and OEMs’ software strategies for recurring revenue through on-demand software features and subscription plans. Safety-critical software interacts with less safety-critical software, and vehicles are connected to the cloud for over-the-air updates. Hardware platforms include a mix of microcontrollers, microprocessors, and systems-on-chip, with a layer of vehicle OS and middleware managing software resources. MathWorks supports the transition to software-defined vehicles by offering solutions for cloud-based development, service-oriented architecture, and integration with Agile/DevOps practices.
- How is the industry addressing skilling and reskilling in the transition from ICE to EV?
The industry is handling skilling and reskilling by adopting various approaches. Firstly, organizations implement internal programs through their Learning and Development departments to reskill engineers from ICE to EV domains. Secondly, they are partnering with universities to skill fresh engineers in the field of electrification. Lastly, many engineers are taking the initiative to self-teach themselves using online materials. MathWorks supports engineers in all three approaches, providing an electrification training curriculum and tools to facilitate learning and understanding of both their tooling and the domain of electrification. They have strong links with academia, offering campus-wide licenses, curriculum design support, and faculty training to bridge the gap between academia and industry.
- How will the charging infrastructure evolve and what are the risks associated with EV adoption?
The charging infrastructure must evolve in three main areas to support EV adoption. Firstly, there is a need for smart investments in enhancing the grid infrastructure to handle surges in demand during common charging times. This requires the development of smart grids to manage charging behaviour intelligently. Secondly, charging infrastructure companies need to establish a significant number of charging stations to meet the demand, with studies suggesting the need for millions of chargers by 2030 in the US, EU, and China alone. Thirdly, OEMs and charging infrastructure companies can expand their revenue streams by offering EV-related products and services, such as energy management and fleet routing solutions. MathWorks observes these challenges and invests in simulating charging protocols, communication, and system validation to support development in this area. Their tools also aid concept evaluations and simulations for optimal charging and infrastructure planning.

Link magazine juni/juli 2023. Thema: Groot maar toch wendbaar. Lees Link magazine digitaal of vraag een exemplaar op bij mireille.vanginkel@linkmagazine.nl
- What are some emerging technologies and investment areas in the Auto Industry for electrification?
The Auto Industry is investing in several emerging technologies. Firstly, big data analytics is being leveraged to extract insights from the vast amount of vehicle-generated data. OEMs are exploring how data can improve vehicle design, provide new features/services, and support decision-making. MathWorks offers a data analytics platform and machine learning capabilities to process and analyze different forms of data. Secondly, AI plays a significant role, particularly in the context of digital twins for batteries. Digital twins can predict battery state-of-charge and state-of-health, provide recommendations to drivers, and address range anxiety. MathWorks provides a comprehensive workflow for AI development and deployment, supporting data preparation, algorithm development, simulation, and embedded device deployment. Lastly, increased virtualization is being adopted to handle the complexity of systems. MathWorks sees demand for virtualization at the vehicle level, where simulations integrate powertrain, dynamics, environment, driver models, and more. This allows for efficient testing and development. The industry seeks solutions to enhance productivity, automation, and development efficiency. MathWorks aims to enable engineers to deliver the next generation of mobility by providing tools and support in these areas.